
First principles on Reaching Customers Through Snipesearch Adclicks
Section 1: How People Use SnipeSearch
Internet Usage Data
The global internet usage statistics are a testament to the digital era’s expansion. According to World Internet Stats, over 4.5 billion people were active internet users as of 2023, accounting for more than 58% of the global population. This staggering number reflects not only a growing dependency on the internet for various activities but also an increased engagement in search activities. Pew Research highlights that a significant portion of internet usage time is dedicated to searching for information, with variations based on regions, age groups, and socio-economic backgrounds.
Search Behavior

The search behavior of internet users is diverse and dynamic. Statista reports that an average internet user conducts between three to four searches per day, translating to approximately 90 to 120 searches per month. This frequency can vary greatly based on age, with younger users (16-24 years) engaging in more searches compared to older demographics.
Gender-wise, data from Internet Live Stats suggests a fairly even distribution, with slight variations based on the search content. Men often search more for technology and sports-related content, while women are more inclined towards healthcare, education, and social networking topics.
Popular Search Genres and Phrases
In 2023, the top genres and phrases searched on the internet provide insight into global interests and concerns. The following were the most popular:
- COVID-19 updates and vaccines
- Climate change and sustainability
- Global political events (e.g., elections, international relations)
- Technology trends (e.g., 5G, AI, IoT)
- Online education and e-learning platforms
- Health and wellness tips
- Financial and investment advice
- Celebrity news and entertainment
- Sports events and updates
- Travel and tourism post-pandemic
The top 20 most searched phrases in 2023 included terms related to these genres, with notable entries like “COVID vaccine near me,” “climate change effects,” “stock market today,” and “best online courses.”
SnipeSearch User Engagement

At SnipeSearch, we’ve observed specific trends in how users engage with our search engine. While we do not retain direct user data, our overall traffic patterns suggest that users spend a significant portion of their online time in search activities. Our platform caters to a diverse audience, with a balanced distribution across genders and a wide range of ages.
The search queries on SnipeSearch align with global trends, reflecting a keen interest in current events, technology, health, and lifestyle topics. Our users value the quick access to information and the privacy-focused approach we offer, making SnipeSearch a preferred choice for many seeking reliable and unbiased search results.
In conclusion, understanding how people use SnipeSearch and other search engines provides crucial insights into internet behaviors globally. It allows us to tailor our services to meet the evolving needs of our users, ensuring a seamless and efficient search experience.
Section 2: How Ads are Delivered on Snipesearch
Ad Placement Strategy on Snipesearch
At Snipesearch, our ad placement strategy is meticulously crafted to ensure a harmonious balance between user experience and effective visibility of advertisements. This approach is thoughtfully differentiated from other platforms such as Meta, Google, and A-ads.
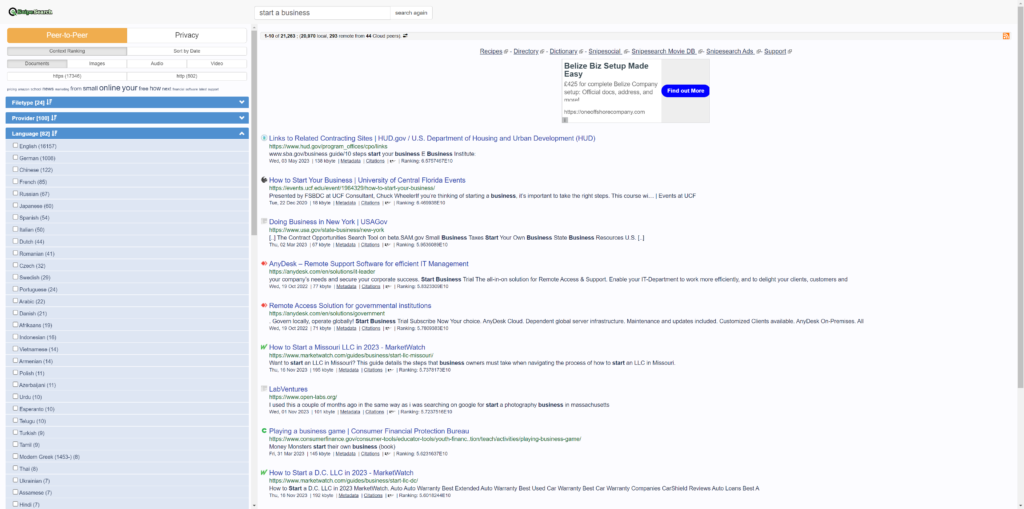
Snipesearch Meta Platform: On our “Snipesearch Meta” platform, we present users with a comprehensive array of search results. Here, advertisements from Snipesearch Adclicks are prominently placed at the top and bottom of the search results, ensuring high visibility. Additionally, a third Snipesearch Adclicks advertisement is strategically positioned to the right of the search results for maximum exposure along with an a-ads advertisement. In some situations on META only some google ads may appear under the top ads in the search results, these will where possible be keyword driven results only for maximum privacy.
In contrast to the top section of Google’s results where ads are intermingled with organic listings, our layout clearly demarcates paid advertisements, maintaining a transparent and user-friendly interface. Furthermore, an A-ads advertisement is also placed on the right, adding to the diversity of ad content presented to our users.
News Section: Within the News section, a unique approach is taken. Advertisements from both Snipesearch Adclicks and A-ads are embedded within the central part of the page, integrated seamlessly within the columns of news articles. This placement ensures that ads are contextually relevant and harmoniously coexist with the content, enhancing user engagement.
Snipesearch Cloud Search: In our Cloud Search feature, we prioritize a minimalist and unobtrusive ad experience. Users will find a single Snipesearch Adclicks advertisement at the top of the page, maintaining the focus on the search results with minimal distractions. This approach particularly appeals to users who favor a straightforward, privacy-centric search experience.
Independent Sections: Across various independent sections on Snipesearch, we maintain a consistent strategy by placing Snipesearch Adclicks ads both at the top and bottom of the pages. This ensures a uniform user experience across different parts of our platform.
User Experience and Interaction
The user experience on Snipesearch is at the forefront of our ad placement strategy. We understand the delicate balance between providing effective ad visibility and maintaining an enjoyable user experience. Our approach is designed to minimize disruption to the user’s search process while still delivering valuable advertising content.
Snipesocial Platform: On Snipesocial, our social media platform, we integrate a mix of ads from Snipesearch Adclicks, A-ads, and other privacy-respecting ad networks. These advertisements are placed in a way that they are noticeable without being intrusive, aligning with the overall ethos of a user-friendly social networking experience.
In comparison to platforms our approach at Snipesearch is to respect the user’s intent and space. We believe this not only enhances the user’s engagement with the ads but also fosters a sense of trust and loyalty towards Snipesearch.
Conclusion
At Snipesearch, we believe in a user-first approach to advertising. Our ad delivery strategy across different platforms, including Snipesearch Meta, Cloud Search, independent sections, and Snipesocial, is a testament to our commitment to providing a search and advertising experience that is respectful, effective, and enhances user trust. By balancing effective ad placement with a non-intrusive user experience, we continue to redefine the standards in the digital advertising space.
Section 3: Do People Really Look at the Ads?

Understanding Ad Impressions and Interactions
The world of online advertising revolves around a critical question: Do people really engage with ads? To answer this, we delve into the realm of ad impressions, click-through rates (CTR), and conversion rates, which are pivotal in understanding user interaction with advertisements.
Ad Impressions and Click-Through Rates: Ad impressions refer to the number of times an ad is displayed, regardless of whether it was clicked or not. The CTR, on the other hand, is a vital metric that measures the percentage of ad impressions that resulted in a click. According to industry benchmarks from Google Ads and Bing Ads, the average CTR across industries hovers around 1.91% for Google and 2.83% for Bing. These figures are indicative of how often people engage with an ad after seeing it.
Conversion Rates: Conversion rate takes a step further by measuring the percentage of clicks that result in the desired action, be it a purchase, sign-up, or download. The average conversion rates again vary by industry, but generally, a good conversion rate is considered to be around 2-5%.
Snipesearch Adclicks: Analyzing Cost-Effectiveness
At Snipesearch, we operate on both CPM (Cost Per Thousand Impressions) and CPC (Cost Per Click) models, with the intent to provide cost-effective advertising solutions. Our CPM rates start at a minimal $0.01, with an average CPM of $0.03. For the CPC model, the starting rate is $0.01, and the average hovers around $0.05.
Calculating Cost Per Conversion: To understand the cost-effectiveness of our CPM and CPC campaigns, let’s delve into a calculation scenario. If our CPM rate is $0.01, and assuming a CTR of 2%, it would mean that out of 1000 ad impressions, 20 result in clicks. If the average conversion rate is 4%, then out of these 20 clicks, we can expect about 0.8 conversions (20 clicks * 4% conversion rate).
Therefore, the cost per conversion in a CPM campaign would be $0.01 (cost of 1000 impressions) divided by 0.8 conversions, resulting in $0.0125 per conversion. Comparatively, in a CPC campaign at $0.01 per click with the same conversion rate, the cost per conversion remains the same, as each click costs $0.01 and the conversion rate is 4%.
Banner Ads vs Text Ads: A Comparative Analysis
The effectiveness of banner ads compared to text ads is a topic of frequent debate in digital marketing circles. Banner ads, with their visual appeal, are thought to be more engaging but suffer from ‘banner blindness’ where users tend to ignore them. On the other hand, text ads, while less visually captivating, are often considered more effective in terms of CTR and conversions.
Research indicates that while banner ads typically have lower CTRs (averaging around 0.1%), they are excellent for brand awareness and retargeting campaigns. Text ads, prevalent in search engine results, often yield higher CTRs due to their relevance to user queries and their prominent placement.
The analysis of ad impressions, interactions, and the cost-effectiveness of different advertising models reveals a complex picture. While each ad type has its strengths and weaknesses, the key lies in understanding the target audience and aligning the ad strategy accordingly. At Snipesearch Adclicks, our low CPM and CPC rates, combined with strategic ad placements, aim to provide an efficient and effective advertising platform for businesses of all sizes. The comparison of banner ads versus text ads further highlights the importance of diversity in ad formats to cater to varied user preferences and objectives.
Section 4: The Appeal of the Snipesearch.net Portal
Features and Benefits of Snipesearch.net
Snipesearch.net stands out in the crowded field of search engines by offering a unique blend of features and benefits that prioritize user experience and privacy. The portal’s key selling points include:
Unbiased News Feeds: One of the most distinctive aspects of Snipesearch is its approach to news delivery. Unlike many other platforms that tailor news feeds based on user behavior, thus creating echo chambers, Snipesearch offers access to global headlines unaffected by user tracking. This ensures a genuinely unbiased and diverse news experience, exposing users to a wider range of perspectives.
Fast Load Times and Access to Billions of Results: Speed is at the heart of Snipesearch’s user experience. The portal is designed for quick access and rapid searches, boasting fast load times that don’t compromise the depth of available information. Users can delve into billions of search results without experiencing delays, making it an efficient tool for both casual browsing and in-depth research.
Customizable Experience Without Mandatory Sign-ins: Snipesearch respects the user’s desire for customization without imposing the need for sign-ins. While users have the option to sign in for a personalized experience, it’s not a prerequisite for using the search engine. This approach respects user autonomy, offering flexibility and convenience.
User Data Control: A Core Principle
At Snipesearch, user data privacy and control are not afterthoughts but foundational principles. We recognize the growing concerns around data privacy and aim to be a bastion of user trust in this regard. Users have full control over their data, with no hidden tracking or data selling. This commitment to privacy sets Snipesearch apart in an era where user data is often commodified.
Snipesearch Cloud and Standalone Indexes
Snipesearch Cloud (Snipesearch.asia): The Snipesearch Cloud, primarily accessible via snipesearch.asia, embodies our philosophy of minimalism and privacy. This version of Snipesearch strips away the news component, focusing solely on the search functionality. It features a simple search box and limits ads to just one per page. The Cloud version does not track personal data, ensuring that users’ search history and preferences do not influence the ads they see. This approach guarantees a private and unintrusive search experience.
Standalone Indexes: In addition to the Cloud, Snipesearch offers standalone indexes that are lightweight and focused on specific niches. These specialized indexes are tailored for users who require in-depth information within particular domains. While smaller in scope, they provide targeted and relevant results, making them invaluable tools for niche research.
Larger Cloud Solutions and Meta Systems: For users who require a more comprehensive search experience, our larger cloud solutions and meta systems incorporate all the data from the standalone indexes. These platforms are ideal for extensive searches that span multiple topics and domains. They offer the breadth of a global search engine while maintaining the depth and specificity of niche indexes.
Snipesearch.net presents a compelling alternative in the search engine market by prioritizing what users value most: speed, privacy, and unbiased information. Our unique approach to news delivery, customizable user experience, and commitment to privacy set us apart in a landscape often dominated by data-driven platforms. Whether through our Cloud version or standalone indexes, Snipesearch offers a search experience that is both expansive and tailored, catering to the diverse needs of modern internet users.
Section 5: Search Engines That Failed Since 2000 and Why
The internet is littered with the remnants of search engines that once promised to revolutionize how we find information online. This section delves into the case studies of five such search engines, examining their rise and fall, and the lessons they leave behind.

AltaVista (URL: www.altavista.com)
Background: Launched in 1995, AltaVista was one of the first widely used search engines, acclaimed for its pioneering technology in search and natural language processing.
Reasons for Failure:
- Lack of Focus on Core Search Functions: AltaVista’s shift towards becoming a web portal diluted its focus from search, confusing users who valued its original utility.
- Failure to Innovate: As Google emerged with a superior, cleaner, and more accurate search technology, AltaVista struggled to keep pace, clinging to outdated algorithms and an increasingly cluttered interface.
- Corporate Turmoil: Acquisitions and changes in ownership led to strategic misalignments, further diverting AltaVista from its core competencies.

Ask Jeeves (URL: www.ask.com)
Background: Launched in 1996, Ask Jeeves distinguished itself with its natural language query approach, inviting users to ask questions directly.
Reasons for Failure:
- Inefficient Algorithm: Despite its novel approach, Ask Jeeves failed to deliver accurate search results consistently, struggling with the complexity of interpreting and responding to natural language queries.
- Branding Issues: The transition from Ask Jeeves to Ask.com in an attempt to appear more serious backfired, alienating users who were attached to the original, more personable brand.
- Competition from More Advanced Search Engines: The rise of Google, with its faster and more reliable search results, overshadowed Ask Jeeves’ unique selling proposition.
Its worth noting that Ask.com is still going, although it lacks the popularity it had, sadly Ask Jeeves was a head of its time, with the aim being to respond to natural language queries, now in the era of large language models like chatGPT the dream they had is far more achievable.
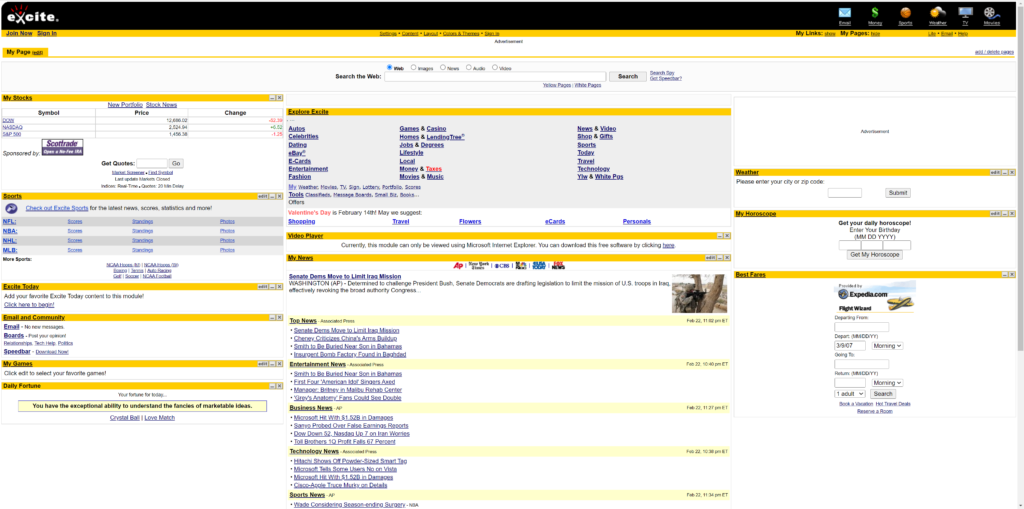
Excite (URL: www.excite.com)
Background: Excite started as a search engine in the early 1990s but quickly transitioned into a web portal, offering a variety of services.
Reasons for Failure:
- Overexpansion and Lack of Focus: The transition to a web portal and the expansion into various internet services stretched Excite thin, leading to a loss of identity and focus.
- Financial Mismanagement: Poor financial decisions, including a failed merger with @Home Network, led to significant debt and eventual bankruptcy.
- Inadequate Search Technology: In the face of evolving search technology, Excite’s search engine remained stagnant, failing to offer competitive search capabilities.

Cuil (URL: www.cuil.com)
Background: Launched in 2008 by former Google employees, Cuil aimed to challenge Google by indexing more pages and providing more comprehensive search results.
Reasons for Failure:
- Overpromising and Underdelivering: Despite its claim to index a larger number of pages than Google, Cuil’s search results were often irrelevant and poorly organized, leading to user dissatisfaction.
- Technical Issues: Cuil faced several technical challenges at launch, including slow load times and frequent server crashes.
- Inadequate Market Research: Cuil misjudged the market’s needs and preferences, focusing too much on beating Google at indexing while neglecting the critical aspects of user experience and accurate search results.
The stories of these failed search engines provide valuable lessons about the rapidly changing digital landscape. Success in this field demands continuous innovation, a clear focus on user needs, and the agility to adapt to market shifts. While these platforms failed to survive, they contributed to the evolution of search technology and set the stage for the current leaders in the industry.
Section 6: Advertising Networks That Failed Since 2000 and Why
The digital advertising landscape has seen its share of ups and downs, with numerous ad networks emerging and disappearing over the years. This section delves into the stories of five such networks, exploring the reasons behind their failures.
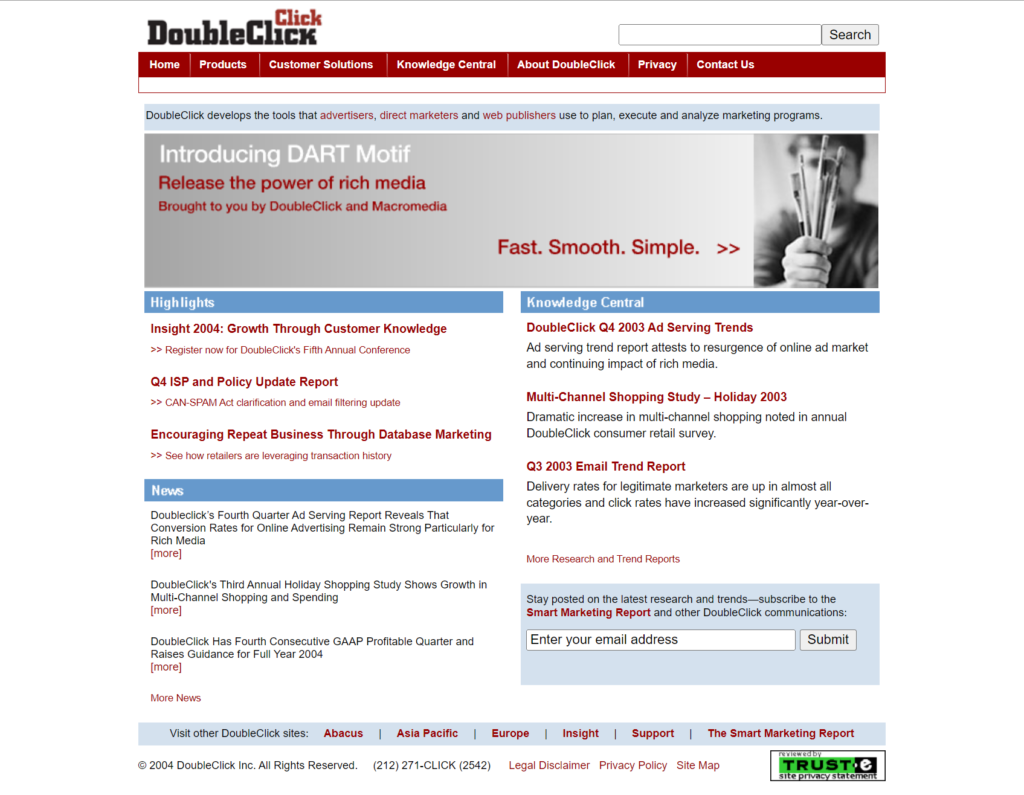
DoubleClick (URL: www.doubleclick.com)
Background: DoubleClick was a prominent ad network known for its web display advertising services.
Reasons for Failure:
- Privacy Concerns: DoubleClick faced severe backlash over privacy issues, particularly related to its use of cookies for tracking user behavior across sites.
- Acquisition and Identity Loss: Acquired by Google in 2007, DoubleClick eventually lost its distinct identity as it became part of the larger Google Ad framework.
- Market Evolution: The digital ad market evolved with new technologies and player; DoubleClick struggled to maintain its initial lead.

AdBrite (URL: www.adbrite.com)
Background: AdBrite started as an internet advertising network, offering a variety of ad formats including banner, interstitial, and video ads.
Reasons for Failure:
- Financial Instability: AdBrite couldn’t sustain its financial model, struggling to keep up with the increasing costs of running a comprehensive ad network.
- Intense Competition: Faced stiff competition from more dominant players like Google Ads and Facebook, leading to a loss in market share.
- Lack of Technological Innovation: AdBrite failed to innovate in a rapidly evolving digital advertising landscape, eventually leading to its shutdown in 2013.
YPN – Yahoo! Publisher Network (URL: publisher.yahoo.com)
Background: YPN was launched by Yahoo! as a direct competitor to Google’s AdSense program, offering contextual ads to publishers.
Reasons for Failure:
- Limited Reach and Beta Status: YPN remained in beta for a prolonged period and was limited to U.S. publishers, significantly limiting its growth potential.
- Inferior Ad Quality and Relevance: Publishers often complained about the lower quality and relevance of ads compared to Google AdSense, leading to lower earnings and dissatisfaction.
- Yahoo’s Decline: As Yahoo! itself started losing its market dominance, YPN also suffered, eventually leading to its closure.
Section 7: Social Networks That Have Failed Since 2000 and Why
The landscape of social media has seen many platforms rise and fall. This section examines the reasons behind the failure of several notable social networks since 2000.
MySpace (URL: www.myspace.com)
Background: Once the largest social networking site, MySpace was renowned for its music-focused features and customizable user profiles.
Reasons for Downfall:
- Facebook’s Rise: The emergence of Facebook, with its cleaner interface and innovative features, heavily eroded MySpace’s user base.
- Overemphasis on Entertainment: MySpace’s heavy focus on music and entertainment alienated users seeking broader social networking features.
- Cluttered Interface: Users often found MySpace’s customizability leading to cluttered and visually overwhelming profiles.
Google+ (URL: plus.google.com)
Background: Launched by Google as a direct competitor to Facebook, Google+ aimed to integrate various Google services with a social layer.
Reasons for Downfall:
- Integration Issues: Forced integration with other Google services like YouTube was met with user backlash.
- Lack of Unique Features: Google+ struggled to differentiate itself significantly from Facebook, leading to low user engagement.
- Data Privacy Scandal: A significant data breach in 2018 hastened the platform’s demise.
Friendster (URL: www.friendster.com)
Background: As one of the first social networks, Friendster initially gained popularity quickly. There was an announcement in 2022 the site would be returning at the time of this publication this had still not occured.
Reasons for Downfall:
- Technical Issues: Friendster suffered from slow page loads and frequent downtime, frustrating users.
- Competitive Overhaul: Friendster failed to innovate and keep pace with emerging rivals like Facebook and MySpace.
- Shift to Gaming: The platform’s pivot to focus on gaming failed to retain its user base, leading to its eventual decline.
Orkut (URL: www.orkut.com)
Background: Owned by Google, Orkut was particularly popular in Brazil and India.
Reasons for Downfall:
- Limited Global Appeal: Orkut failed to gain significant traction outside of its key markets.
- Rise of Facebook: The global dominance of Facebook overshadowed Orkut’s presence.
- Privacy Concerns: Issues with spam, fake profiles, and privacy concerns led to user distrust.

Vine (URL: vine.co)
Background: Vine revolutionized social media with its short, looping video format.
Reasons for Downfall:
- Twitter’s Acquisition and Neglect: Post-acquisition by Twitter, Vine suffered from a lack of development and innovation.
- Competition from Instagram: Instagram’s introduction of video features directly competed with Vine’s unique selling point.
- Monetization Issues: Vine struggled to monetize effectively, impacting its sustainability.
Bebo (URL: www.bebo.com)
Background: Bebo was a social networking website launched in 2005, known for its personalization features.
Reasons for Downfall:
- Acquisition Woes: After its acquisition by AOL, Bebo didn’t receive the needed strategic direction or investment.
- Lack of Innovation: Bebo failed to innovate and keep up with the evolving social media landscape.
- User Migration: Users migrated to more engaging and rapidly growing platforms like Facebook.

Google Buzz (URL: buzz.google.com)
Background: Google Buzz was an early attempt by Google to enter the social networking space.
Reasons for Downfall:
- Privacy Issues: Google Buzz faced immediate criticism for its privacy flaws, particularly its automatic addition of Gmail contacts.
- Integration Backlash: The forced integration with Gmail was unpopular among users.
- Market Saturation: The market was already dominated by established players, leaving little room for Buzz.

Yik Yak (URL: www.yikyak.com)
Background: Yik Yak was an anonymous social media app that gained popularity for its local bulletin board-style interface. At the time of this publication yik yak was attempting another comeback
Reasons for Downfall:
- Cyberbullying and Controversies: The app became infamous for cyberbullying incidents, raising serious concerns.
- Identity Shift: Attempting to shift away from anonymity, Yik Yak lost its unique appeal to users.
- Decline in User Base: The controversies and changes led to a rapid decline in its user base.
Conclusion
These case studies of failed social networks underscore the importance of continuous innovation, user privacy, technical stability, and adapting to market needs. They also highlight the challenges of maintaining user engagement in the face of growing competition and changing social media trends. Understanding the dynamics of search engines and social media can help you understand which networks work and why and allow you to intelligently use this to pick partners to market on. Its also worth noting that small networks should not be avoided for simply being small as you can reach untapped audiences in these areas. Simply dont spend too much money on minor networks unless something about them seems to have a unique selling point which many of these networks did not.

Section 8: Why Non-Intrusive Ad Networks Like Snipesearch Adclicks Are So Effective
Request marketing is a strategic approach in the world of digital advertising, where ads are tailored to align with the specific interests or needs of the user at the moment of their search. It’s a form of precision marketing that connects advertisers with potential customers who are actively seeking what they have to offer. In this context, platforms like Snipesearch become invaluable tools in bridging the gap between consumer desire and business offerings.
Understanding Request Marketing
- The Concept:
- At its core, request marketing involves displaying ads that correlate directly with the user’s current search query or recently expressed interests.
- This method is highly effective because it taps into the existing intent of the user, offering solutions or products that align with their immediate needs.
- Historical Perspective:
- The evolution of request marketing can be traced back to the early days of search engines and online directories.
- Over time, the sophistication of targeting technologies and algorithms has greatly enhanced the precision and effectiveness of this marketing strategy.
Efficiency and Conversion Rates
- High Conversion Potential:
- Request marketing typically sees higher conversion rates compared to traditional advertising, given its targeted nature.
- Users presented with ads that match their search intent are more likely to engage and proceed to the transaction phase.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- In terms of cost, request marketing can be incredibly efficient, particularly on platforms with competitive pricing models like Snipesearch.
- The $0.01 CPM (Cost Per Mille) and $0.01 CPC (Cost Per Click) rates on Snipesearch make it an accessible and cost-effective option for advertisers of all scales.
Snipesearch as a Request Marketing Platform
- Tailored Advertising:
- Snipesearch Adclicks specializes in aligning ads with user queries, ensuring that advertisements are relevant and timely.
- This relevance increases the likelihood of user engagement and conversion, as ads align with the immediate interests or needs of the user.
- Budgeting for Conversions:
- For a business aiming for 1000 conversions through a request marketing campaign on Snipesearch, the cost can be surprisingly manageable.
- With a $0.01 CPM or CPC rate, businesses can achieve significant reach and engagement without exhausting their marketing budget.

Calculating Campaign Costs
- Estimating Conversion Costs:
- To estimate the cost of achieving 1000 conversions, one must consider factors like the average click-through rate (CTR) and conversion rate specific to their industry or product.
- For instance, if the average CTR is 2% and the conversion rate is 5%, the calculations would determine the number of impressions or clicks required to achieve the desired conversions.
- Yearly Budgeting:
- Based on these metrics, businesses can formulate a yearly budget for their request marketing campaign on Snipesearch.
- The affordability of Snipesearch’s advertising rates allows for extensive reach and frequency, maximizing the campaign’s potential for success.
Assumptions:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): 2%
- Conversion Rate: 5%
- Cost Per Click (CPC) on Snipesearch: $0.01
- Cost Per Mille (CPM) on Snipesearch: $0.01 (per 1000 impressions)
Calculations:
Using CPC:
- Clicks Needed for One Conversion:
- If the conversion rate is 5%, it means 5 out of every 100 clicks result in a conversion.
- Therefore, for one conversion, you need 20 clicks (100 / 5).
- Total Clicks Needed for 1000 Conversions:
- For 1000 conversions, you need 20,000 clicks (1000 conversions * 20 clicks per conversion).
- Total Cost for 20,000 Clicks:
- At $0.01 per click, 20,000 clicks will cost $200 (20,000 clicks * $0.01).
Using CPM:
- Impressions Needed for One Click:
- If the CTR is 2%, it means 2 out of every 100 impressions result in a click.
- Therefore, for one click, you need 50 impressions (100 / 2).
- Total Impressions Needed for 20,000 Clicks:
- For 20,000 clicks, you need 1,000,000 impressions (20,000 clicks * 50 impressions per click).
- Total Cost for 1,000,000 Impressions:
- At $0.01 per 1000 impressions, 1,000,000 impressions will cost $10 (1,000,000 / 1000 * $0.01).
Summary:
- Budget Using CPC Model: To achieve 1000 conversions, you would need to budget approximately $200, assuming each click costs $0.01.
- Budget Using CPM Model: To achieve the same number of conversions, the campaign would cost significantly less, around $10, but this assumes a very high efficiency in converting impressions to clicks and then to conversions.
While the CPM model appears more cost-effective, it’s important to note that achieving a high CTR and maintaining a consistent conversion rate can be challenging. In contrast, the CPC model offers more predictability in costs relative to conversions. The choice between CPC and CPM would depend on the specific goals of the campaign and the historical performance data of similar campaigns.
For a business aiming for 1000 conversions through a request marketing campaign on Snipesearch, the cost can be surprisingly manageable.
With a $0.01 CPM or CPC rate, businesses can achieve significant reach and engagement without exhausting their marketing budget.
Request marketing represents a potent and efficient avenue for reaching potential customers in a targeted and timely manner. Platforms like Snipesearch facilitate this approach by offering cost-effective advertising solutions that resonate with user search behavior. By understanding the mechanics and potential of request marketing, businesses can craft campaigns that not only reach but also resonate with their intended audience, driving meaningful conversions at an optimal cost.

Section 10: Adapting Your Campaign with Feedback Cycles
In the realm of digital advertising, constant adaptation and optimization are keys to success. While access to detailed user data is often seen as a crucial element of campaign optimization, it’s not the only way to enhance your advertising efforts. By utilizing feedback cycles effectively, advertisers can significantly improve their campaigns even without deep data analytics. This section delves into the importance of feedback cycles, how to interpret campaign data effectively, and the steps to adjust campaigns for optimal performance.
Importance of Feedback Cycles
- Real-Time Adaptation: Digital marketing landscapes change rapidly. What works today might not work tomorrow. Regular feedback allows for swift adaptations to these changes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By identifying underperforming elements of your campaign early, you can allocate your budget more effectively, reducing wastage on ineffective strategies.
- Competitive Advantage: In a saturated market, the ability to quickly adjust your strategies based on performance data can give you an edge over competitors who may be slower to react.
Monitoring Campaign Performance
- Keyword Performance Analysis: Keep a close eye on which keywords are driving traffic to your website. High-click keywords indicate audience interest and relevance.
- Landing Page Conversion Rates: Evaluate which landing pages are converting visitors into customers. High-converting pages should be a model for future content.
- Click-Through Rates (CTR): A vital metric that shows how compelling your ad is to your target audience. Low CTRs might indicate a need for more engaging or relevant ad copy or visuals.
Implementing Data-Driven Changes
- A/B Testing: Regularly test different versions of your ads and landing pages to determine which elements resonate best with your audience.
- Refine Ad Copy and Design: Use feedback to tweak your ad’s messaging and visual elements. Sometimes, even minor changes in the call-to-action or color scheme can significantly impact performance.
- Keyword Optimization: Adjust your focus on keywords based on performance data. Consider both high-performing keywords and those with potential that are underutilized.
Establishing a Feedback Loop
- Set Regular Review Periods: Schedule consistent intervals to review campaign data. This could be daily, weekly, or bi-weekly, depending on the campaign scale.
- Utilize Analytics Tools: Leverage tools provided by Snipesearch Adclicks and other platforms to gather comprehensive data on your campaign’s performance.
- Gather Consumer Insights: If possible, collect direct feedback from your audience through surveys or social media interactions to understand their perception of your ads.
Continual Learning and Adaptation
- Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keep up-to-date with the latest digital marketing trends and consumer behaviors to ensure your campaigns remain relevant.
- Iterative Process: View feedback cycles as an ongoing process. Continually refine and adapt your campaigns based on the latest data and insights.
- Record and Analyze Past Campaigns: Maintain a record of past campaigns and their performances. Analyzing these can provide valuable insights for future strategies.

Section 11: Campaign Strategy Checklist
When launching a campaign, especially on platforms like Snipesearch Adclicks, it’s crucial to have a structured approach. This 20-point checklist ensures that your campaign is well-planned, organized, and set up for success.
- Campaign Settings: Ensure your campaign settings align with your business goals (budget, language, category, location, keywords).
- Organized Labeling: Are your campaigns well-labeled for easy identification and modification?
- Success Metrics: Define how you will measure success (clicks, sales, leads, sign-ups).
- Long-Term Tracking: If sales aren’t immediate, have a plan to track inquiries and follow-up conversions.
- Exit and Entry Page Analysis: Monitor the entry and exit pages on your site to understand user behavior.
- Ad Copy Testing: Do you have a strategy for A/B testing your ad copy?
- Compliance with Adclicks TOS: Ensure you’re following Snipesearch Adclicks’ rules and terms of service.
- Bid Assessment: Regularly evaluate if your bids are too high or low based on traffic and budget usage.
- Keyword Strategy: Have a clear plan for selecting and adding keywords.
- ROI Tracking: Are you tracking the ROI for each campaign, keyword, or ad group?
- Keyword Adjustment: Adjust your keywords based on ROI insights.
- Target Audience Definition: Clearly define your target audience to ensure ad relevance.
- Creative Elements: Ensure your ads have compelling visuals and copy.
- Landing Page Optimization: Are your landing pages optimized for conversion?
- Mobile Compatibility: Ensure your ads and landing pages are mobile-friendly.
- Frequency Capping: Set limits on how often the same user sees your ad to avoid ad fatigue.
- Seasonal Adjustments: Plan for seasonal variations in your market.
- Competitor Analysis: Regularly check what competitors are doing and adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Performance Review Schedule: Set a regular schedule to review and adjust campaigns.
- Feedback Loop: Have a system in place to gather and implement feedback from campaign performance.
This checklist provides a comprehensive approach to campaign management, ensuring all critical aspects are covered for optimal performance and ROI.
Conclusion
In wrapping up this extensive exploration of “First Principles on Reaching Customers Through Snipesearch Adclicks,” we’ve delved deep into the nuances of online marketing and advertising. This guide has taken us through various realms of digital marketing, from understanding user behavior on SnipeSearch to the intricate details of non-intrusive ad networks like Snipesearch Adclicks. We’ve analyzed failed platforms, celebrated successes, and provided actionable strategies for advertisers.
A key takeaway from our journey is the evolution of user expectations and privacy standards in digital marketing. Users today are not just passive recipients of advertising but active participants seeking relevance, respect, and privacy. Platforms like Snipesearch are at the forefront of this change, emphasizing user privacy while still offering effective advertising solutions.
The landscape of digital marketing is complex and ever-evolving. It’s a dance of balancing user privacy with effective advertising, understanding search engine mechanics, and adapting to changing market dynamics. This guide has hopefully illuminated the path for advertisers and marketers, providing a comprehensive toolkit to navigate these waters.
As we conclude, remember that the world of digital marketing is not static. It’s a vibrant ecosystem that requires continuous learning, adaptation, and a keen understanding of both technology and human behavior. Whether it’s through the nuanced use of Snipesearch Adclicks or understanding the broader context of the SEM ecosystem, success lies in the details and a willingness to evolve.
Remember, the principles outlined in this guide are just the beginning. The real adventure lies in applying these concepts, experimenting, and finding what resonates with your audience. Here’s to your success in harnessing the power of Snipesearch Adclicks and making a mark in the digital world!